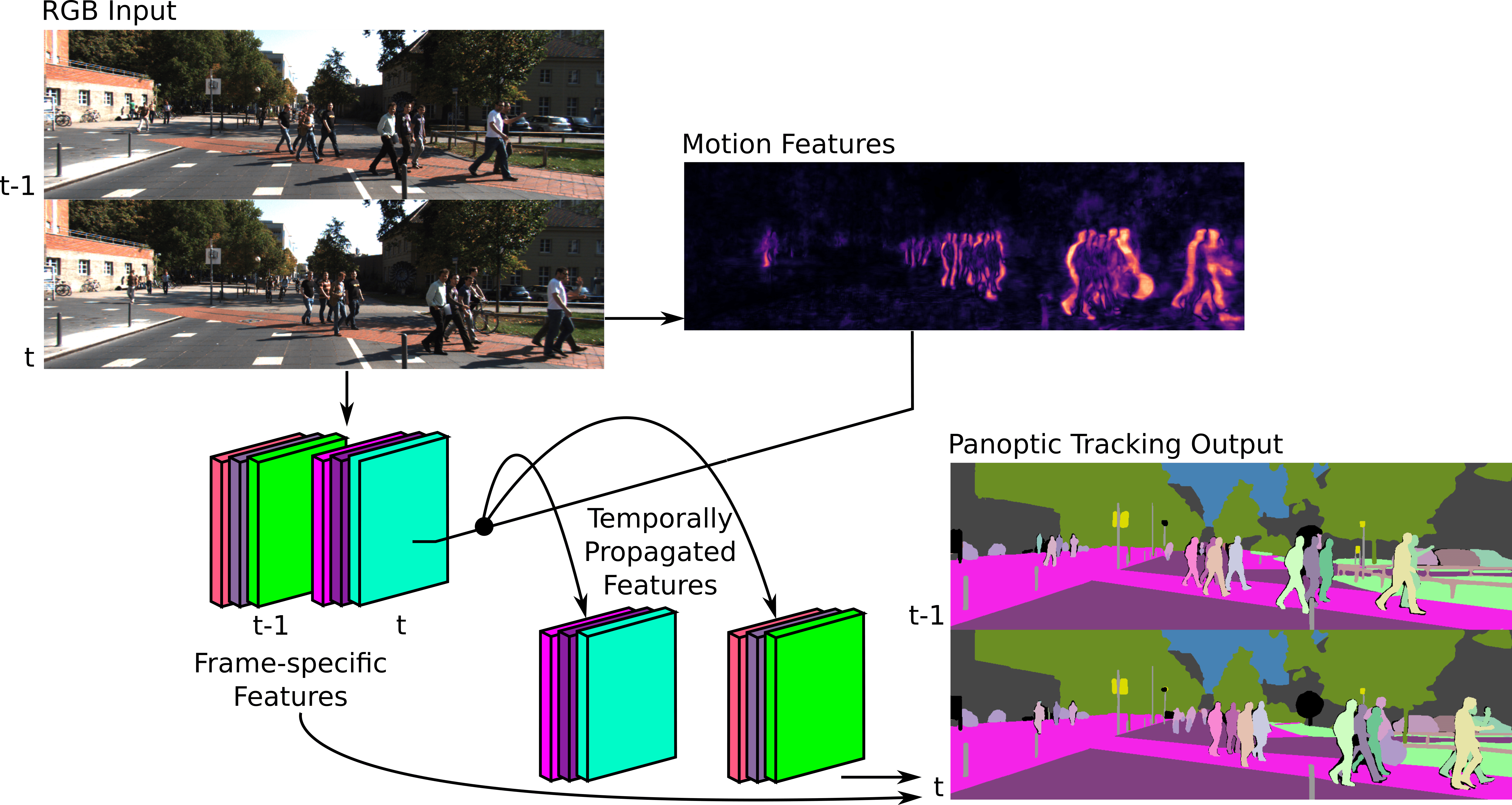
Panoptic tracking enables pixel-level scene interpretation of videos by integrating instance tracking in panoptic segmentation. This provides robots with a spatio-temporal understanding of the environment, an essential attribute for their operation in dynamic environments. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for panoptic tracking that simultaneously captures general semantic information and instance-specific appearance and motion features. Unlike existing methods that overlook dynamic scene attributes, our approach leverages both appearance and motion cues through dedicated network heads. These interconnected heads employ multi-scale deformable convolutions that reason about scene motion offsets with semantic context and motion-enhanced appearance features to learn tracking embeddings. Furthermore, we introduce a novel two-step fusion module that integrates the outputs from both heads by first matching instances from the current time step with propagated instances from previous time steps and subsequently refines associations using motion-enhanced appearance embeddings, improving robustness in challenging scenarios. Extensive evaluations of our proposed \netname model on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that it achieves state-of-the-art performance in panoptic tracking accuracy, surpassing prior methods in maintaining object identities over time.





